Local and Global Server Load Balancing with NGINX Plus and Cedexis
{$inline_image}
Today’s web applications run at a scale and speed that was hard to imagine just a few years ago. To support them, organizations host digital assets in many environments: regions in a single public cloud, multiple public and private clouds, content distribution networks (CDNs), company‑owned and leased data centers, and others. They move digital assets between hosts to meet business needs relating to delivery speed, reliability, and cost.
NGINX works on these problems from the bottom up. From individual web servers to load balancers to clusters, NGINX users create aggregations of servers to deliver services in specific regions and around the world. Cedexis works on the same problems from the top down. Cedexis helps customers manage their online assets to support service delivery on a global scale.
NGINX and Cedexis have now announced the NGINX Plus & Cedexis Local + Global Server Load Balancing (L+GSLB) solution. With this solution, you can fully automate the delivery of your full application stack. Your stack becomes responsive to a complete set of metrics: NGINX Plus health‑check data for local load balancers, and customer‑centric real user monitoring data and synthetic testing data from Cedexis, plus any other data feed, all of which serve as input to application delivery logic incorporating your business rules.
With the NGINX Plus & Cedexis L+GSLB solution, when one or more servers go down within a single region or globally, traffic can automatically be routed around impacted servers and locations. When the servers come back up, previous traffic patterns can be automatically restored. Traffic can be made similarly responsive to business rules that address cost, response time, availability, and other metrics. You can try it yourself with the NGINX Plus & Cedexis L+GSLB demo.
Ensuring Low Latency and High Availability for NGINX Plus Users
The software‑defined Cedexis Global Server Load Balancer (GSLB) platform is a control plane and abstraction layer for DevOps and IT Operations. It provides automated, predictive, and cost‑optimal routing of your apps, video, and web content.
The platform is powered by both real user monitoring (RUM), which leverages the world’s largest community of live user‑experience data, and synthetic monitoring. The Cedexis GSLB platform can also ingest data feeds from many other data sources like application performance monitoring (APM), clouds, and CDNs – and now, critically, NGINX Plus local load balancer health checks.
NGINX Plus users can access the power of the Cedexis GSLB platform, and Cedexis users can see what’s going on inside the data center. This helps a great deal when load balancing across a combination of data centers, clouds, and CDNs (or within any one of them).
Implementing the NGINX Plus & Cedexis Local + Global Server Load Balancing Solution
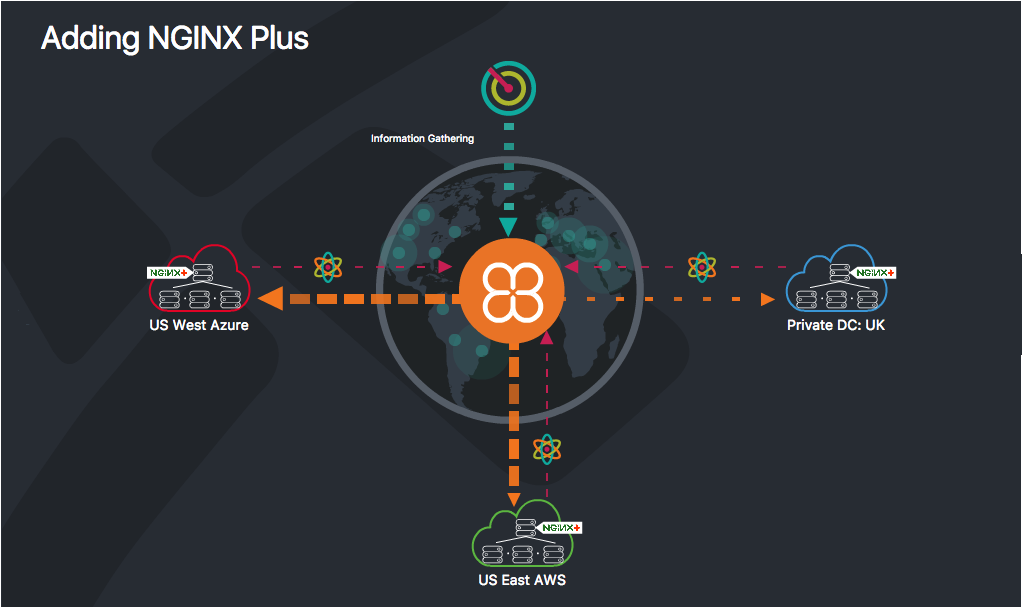
Inside a single public cloud region (such as AWS West‑Oregon), you can set up NGINX Plus for high availability (HA) in a data center. This NGINX Plus configuration provides best‑in‑class, HA load balancing inside that particular cloud region. But as recommended by public cloud providers like AWS, most cloud‑based apps reside in more than one public cloud zone or region, or in a hybrid‑cloud infrastructure including at least one data center. The NGINX Plus & Cedexis L+GSLB solution automatically extends to the second, third, and additional regions as they’re added, with no further setup required.
Inside a public cloud region and data center, such as US West Azure and US East AWS in the figure below, each NGINX Plus instance continuously collects data about the health of the resources where it is installed. That data is then transmitted to Cedexis, where it’s used to make better global traffic management (GTM) routing decisions.
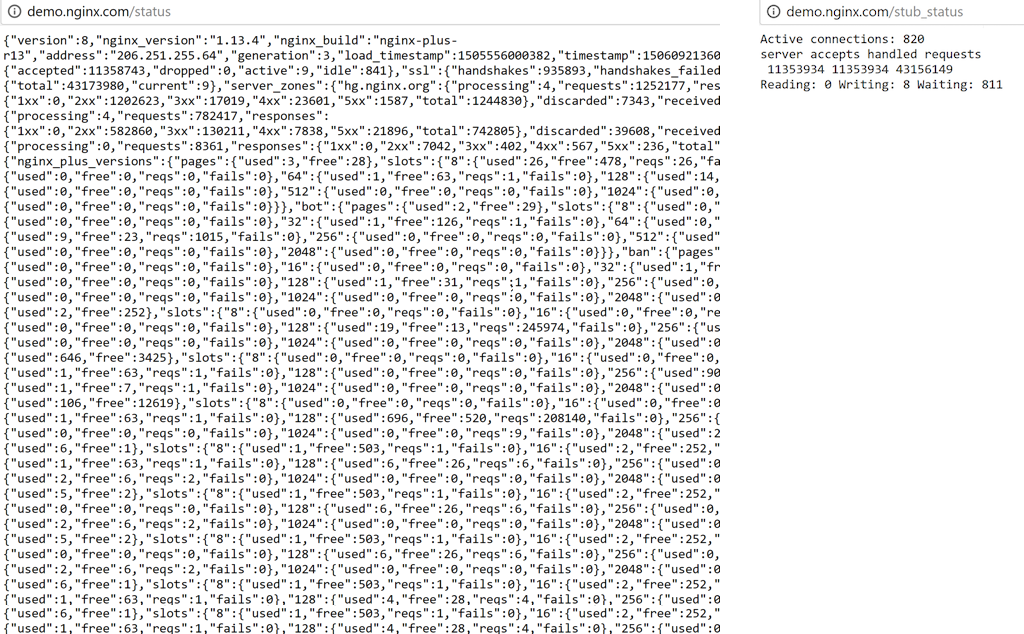
NGINX Plus generates real‑time activity data that provides DevOps teams with both load and performance metrics. Cedexis is able to ingest this data through a RESTful JSON API and incorporate it into the GTM algorithm. DevOps teams can use this data any way they want to inform the routing of apps. The left side of the following graphic gives you an idea of the massive amount of activity monitoring data that is available to Cedexis GTM from NGINX Plus, as opposed to open source NGINX (the right side of the graphic).
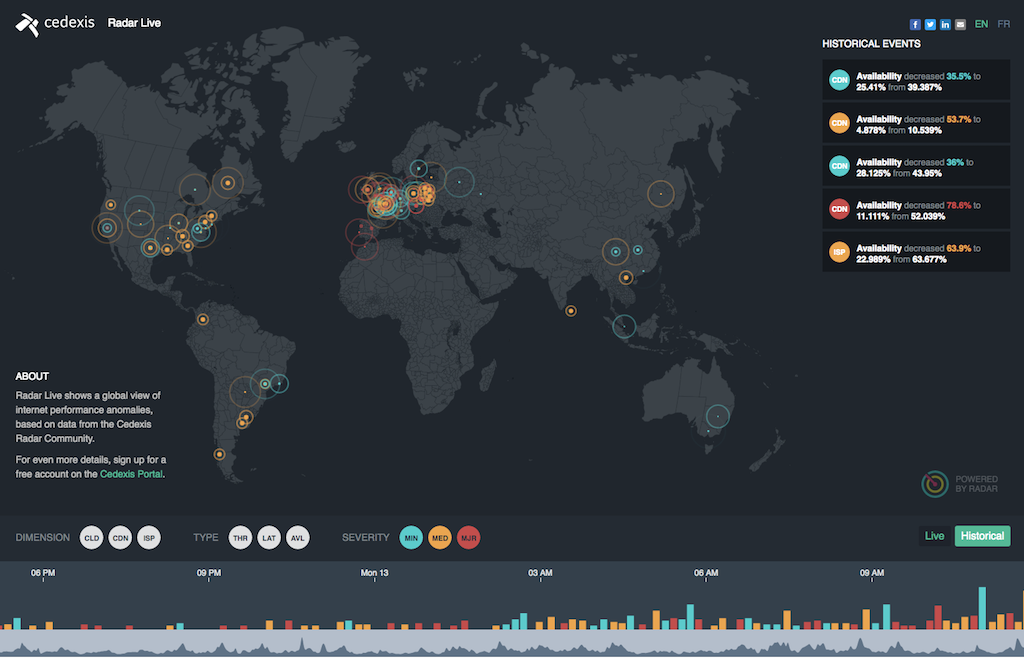
How It Works: Real-Time Decisions Based on Cedexis Radar and NGINX Plus
To walk you through how the integrated NGINX Plus & Cedexis solution works, let’s say a SaaS company uses one data center and two public clouds across the globe to deliver services to their worldwide customer base. It’s likely they are set up to use traditional geo‑based routing only. Essentially, this means that app data is routed to the data center or cloud closest to the end user. When things are working well, this is probably OK. However, when problems arise, this simple setup can make them worse.
The Cedexis Radar service continually collects traffic data from all over the world, related to hundreds of millions of web users, not just those using any one customer’s data center and clouds. The Cedexis GTM platform uses this data to route traffic to the data center or cloud that offers the fastest‑responding servers for end users. This means that in many cases content is delivered from a source that is not the closest geographically, if that provides the best customer experience.
As an example, consider the setup in the graphic below, with NGINX Plus running in two public cloud regions in the US and in a data center in the UK. If Cedexis Radar detects network traffic issues between continental Europe and the UK, Cedexis can use that data to route European traffic to the two US cloud regions because they are now closer (in terms of user experience) than the UK data center. “Micro‑outages”, often undetected by Ops teams until a forensic analysis takes place, are dealt with automatically, without any adverse impact on end users.
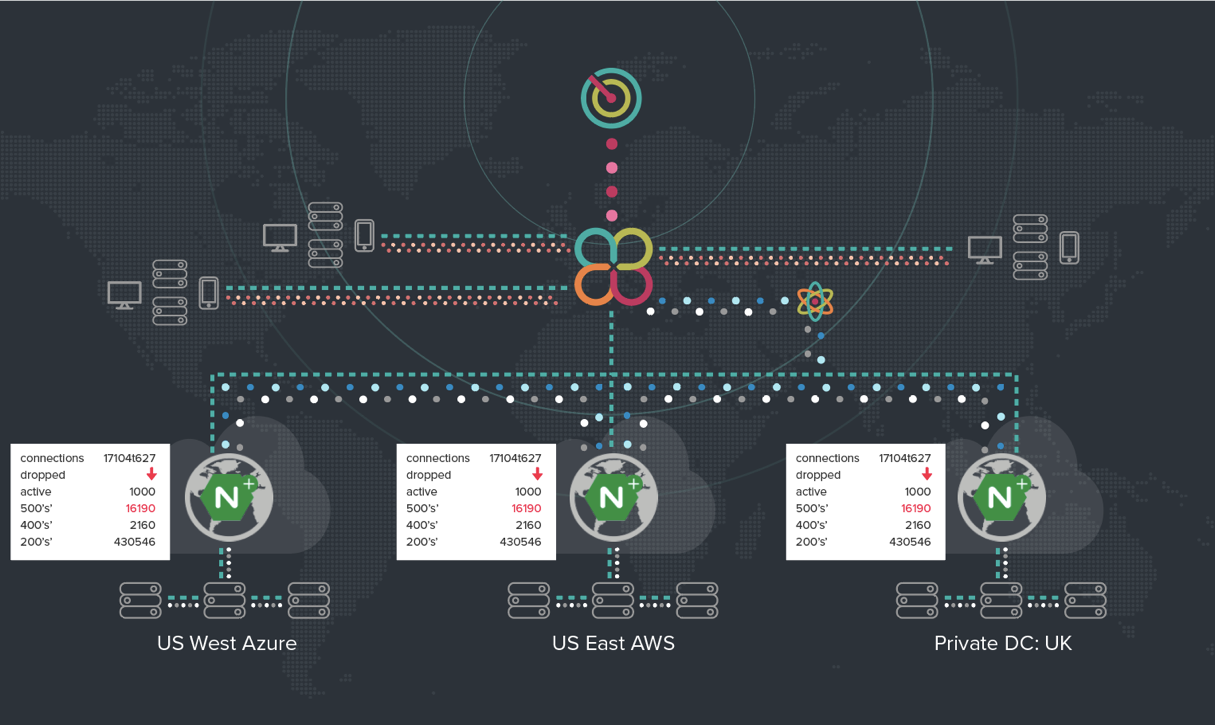
Each NGINX Plus instance collects data about the health of the resources where it is installed, which is automatically ingested by Cedexis to inform GTM. Suppose, for example, that a data center has several servers that are dropping connections, as shown in the following graph.
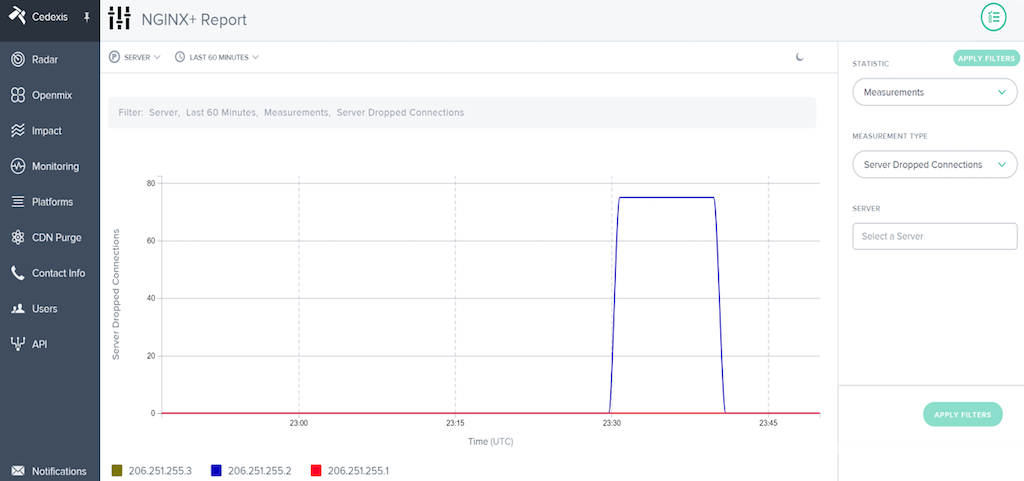
Cedexis automatically adjusts and readjusts its decisions, in real time, to route traffic around the impacted servers, as depicted in this graph.
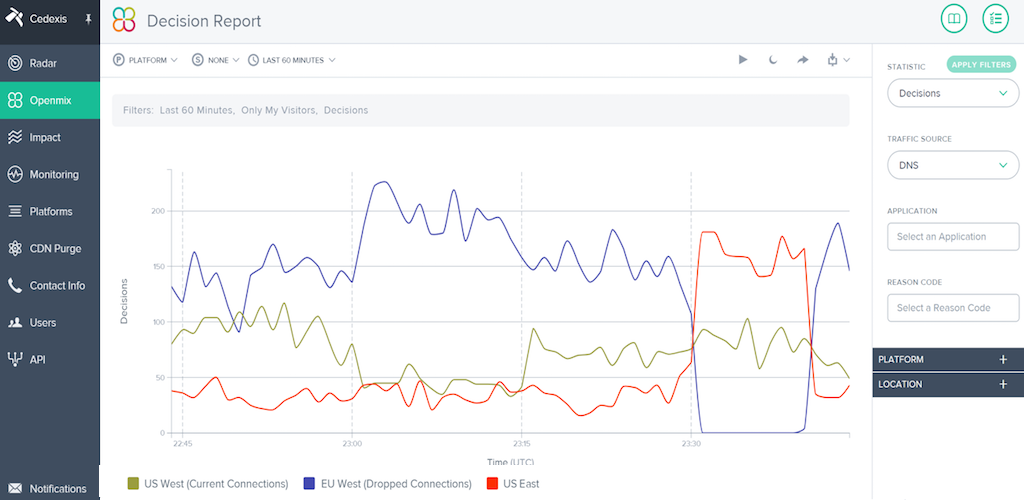
When things return to normal, or a mitigation is implemented, the traffic is automatically restored to the original resource. DevOps teams can sleep soundly, knowing this is taking place even when they are out of the office.
Check out this demo to see for yourself how NGINX Plus and Cedexis deliver integrated, full‑stack load balancing. For details, see our Solution Brief or talk to a solutions expert at Cedexis or NGINX.
The post Local and Global Server Load Balancing with NGINX Plus and Cedexis appeared first on NGINX.
Source: Local and Global Server Load Balancing with NGINX Plus and Cedexis






Leave a Reply